On the 8th of November 2022 .NET 7 was released, including .NET MAUI (.NET Multi-platform App UI). In this blogpost we will investigate the differences between Xamarin.Forms and its successor.

What is its purpose and how it evolved in the framework and platform it is now? What will the future bring for these two environments? We will end this blog post with the advantages of .Net Maui over Xamarin.Forms and the evolution of Xamarin.
Xamarin
Xamarin was introduced in May 2011 with the foundation of the Xamarin Company. It was created with a commercial purpose, until it was acquired by Microsoft in 2016. It was based on the mono project introduced in 2001.
The platform is used for cross-platform mobile applications where 90% of the code is shared over multiple platforms like ios, android and windows. It is a single-language platform, C#, which opened the path for cross platform development in the .Net ecosystem and all his advantages. The purpose of Microsoft was to migrate Xamarin in the .NET Base Class Library.
Xamarin.Forms
This is an open source UI framework that allows developers to create user interfaces as an abstraction layer over native controls on each platform (Android, IOS or windows). The framework uses one shared project, where 90% of the code resides, and platform specific projects for native development. With the release of the new framework(.NET MAUI) support will end on the 1st of may 2024, with Android 13 and XCode 14 as the latest supported native SDK’s.
.NET MAUI
With the introduction of Xamarin and Xamarin.Forms out of the way, we can now look at .Net Maui itself. This open source UI framework is developed by the same team. With .NET 7, this rewrite of Xamarin.Forms had its first official release on the 8th of november. With its release Xamarin is completely pulled into the .NET base class library as part of the journey to one .NET. This new UI framework of .NET contains several changes, but still has some basic features that already existed in Xamarin Forms like controls, Shell, Templates, … .
What are the differences with Xamarin.Forms
Project structure
The biggest difference is the project structure, as Xamarin.Forms has multiple projects .NET MAUI has only one project. As you can see in the underlying example.
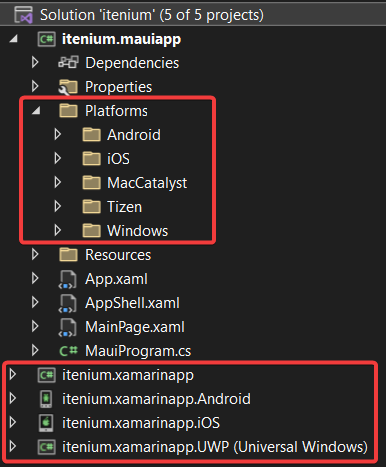
More target platforms are supported
As you can see in the project structure above, .NET MAUI supports more targets than its predecessor.
.NET CLI support
You can create, build and emulate you Maui application from within .NET CLI. Therefore you need to install the .Net SDK. download here
With the SDK installed you can run the next command for creating a new maui project in the current folder.
dotnet new maui
.NET 7
As Maui is build in inside .Net 7, it takes advantage of it. It does not only support xaml hot reload, but also .Net hot reload. It enables faster app startup through improved memory usage.
Controls with handlers
Controls are managed through a handler architecture which makes it loosely coupled from the native controls, as Xamarin.Forms makes use of renderers which are tightly coupled.
Resources
Because .NET MAUI only has one project, resource management is simplified in that one location. Images do not need to be maintained in each platform specific project but are also manageable from within that single project. Adding an svg file is sufficient to add new resources.
Blazor
With .NET MAUI you can build Blazor applications with C# instead of javascript.
Conclusion
.NET MAUI is the result of pulling Xamarin into the .NET BCL. It contains many features from Xamarin Forms and has many improvements to show the potential of this new UI framework.
Extras
Other interesting reads

