Quick tutorial about creating xlsx Excels with C# and the ClosedXML nuget package.
The blog posts only covers the most important functionality. More extensive code examples can be found in the GitHub project.
Quick tutorial about creating xlsx Excels with C# and the ClosedXML nuget package.
The blog posts only covers the most important functionality. More extensive code examples can be found in the GitHub project.


Install-Package ClosedXML
It basically provides a more intuitive and user-friendly interface compared to the OpenXML API it’s built on top off. Hence the name ;)
I used to be a big fan of EPPlus but since it is no longer free, this aims to be a pretty much 1 to 1 conversion of our EPPlus blog series.
If you’re migrating, AI is pretty good at converting EPPlus code to ClosedXML, for most (simple) use cases, it just works!
Documentation is a bit in limbo. The Github wiki contains most examples but they are not always up to date, as for some things the API has changed slightly.
The ReadTheDocs is the new documentation and while it does go into a lot more detail for some particularities, it does not cover everything and has a lot less examples.
cell.DataValidation ⮕ cell.CreateDataValidation()cell.Comment ⮕ cell.CreateComment()There is also the ClosedXML.Examples console project in the source code.
git clone https://github.com/closedxml/closedxml
cd closedxml
dotnet run --project ClosedXML.Examples --framework net8.0
This creates all the example Excels in ClosedXML.Examples/bin/Debug/net8.0/Created, you can then compare the code with the actual output and go from there!
using ClosedXML.Excel;
using var workbook = new XLWorkbook();
IXLWorksheet sheet = workbook.AddWorksheet("MySheet");
// Setting & getting values
IXLCell firstCell = sheet.Cell(1, 1);
firstCell.Value = "will it work?";
sheet.Cell("A2").FormulaA1 = "CONCATENATE(A1," ... Of course it will!")";
Assert.That(firstCell.GetString(), Is.EqualTo("will it work?"));
// Numbers
var moneyCell = sheet.Cell("A3");
moneyCell.Style.NumberFormat.Format = "$#,##0.00";
// Or use a predefined style
// See: https://github.com/closedxml/closedxml/wiki/NumberFormatId-Lookup-Table
moneyCell.Style.NumberFormat.NumberFormatId = (int)XLPredefinedFormat.Number.Precision2WithSeparator;
moneyCell.Value = 1500.25M;
// Easily write any Enumerable to a sheet
var data = new[]
{
new { FunctionName = "CHAR", Description = "Returns the character specified by the code number" },
new { FunctionName = "FIND", Description = "Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive)" },
};
sheet.Cell("A4").InsertTable(data, true);
sheet.Cell("A12").InsertData(data);
// Styling cells
var someCells = sheet.Cells("A1,A4:B4");
someCells.Style.Font.Bold = true;
someCells.Style.Font.SetFontColor(XLColor.Ivory);
Assert.That(XLColor.Ivory, Is.EqualTo(XLColor.FromColor(Color.Ivory)));
// XLColor also has static methods FromArgb, FromHtml, FromKnownColor etc
// See: https://github.com/closedxml/closedxml/wiki/ClosedXML-Predefined-Colors
someCells.Style.Fill.SetPatternType(XLFillPatternValues.Solid);
someCells.Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.Navy;
// Full control over filtering
// See: https://docs.closedxml.io/en/latest/features/autofilter.html
int lastCol = sheet.ColumnsUsed().Last().ColumnNumber();
sheet.Range(1, 1, 1, lastCol).SetAutoFilter();
sheet.ColumnsUsed().AdjustToContents();
workbook.SaveAs("basicUsage.xslx");
At first I didn’t quite understand why there were both properties and “setter functions” for so many things. It is a bit overkill but it does allow the following code:
someRange.Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.FromHtml("#F0F4FF");
someRange.Style.Border.RightBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Thin;
someRange.Style.Border.RightBorderColor = XLColor.FromHtml("#D4D4D4");
To also be written like:
someRange.Style
.Fill.SetBackgroundColor(XLColor.FromHtml("#F0F4FF"))
.Border.SetRightBorder(XLBorderStyleValues.Thin)
.Border.SetRightBorderColor(XLColor.FromHtml("#D4D4D4"));
Which does look better! 😃
using var workbook = new XLWorkbook();
var sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("MySheet");
// One cell
IXLCell cellA2 = sheet.Cell("A2");
var alsoCellA2 = sheet.Cell(2, 1);
Assert.That(cellA2.Address.ToString(), Is.EqualTo("A2"));
Assert.That(cellA2.Address, Is.EqualTo(alsoCellA2.Address));
// Get the column from a cell
Assert.That(cellA2.Address.ColumnNumber, Is.EqualTo(1));
// To really get the column: sheet.Column(1) or sheet.Column("A")
// A range
IXLRange ranger = sheet.Range("A2:C5");
var sameRanger = sheet.Range(2, 1, 5, 3);
Assert.That(ranger.RangeAddress, Is.EqualTo(sameRanger.RangeAddress));
//sheet.Cells("A1,A4") // Just A1 and A4
//sheet.Ranges("A1,A4") // Same, but as a range
//sheet.Row(1) // A row
//sheet.Range("A:B") // Two columns
// Linq
// Not so performant to use standard linq
sheet.Range("A1:A5").Cells().Where(cell => cell.HasComment);
// Better to use the ClosedXML specific functions
// Also: RowsUsed, FirstColumnUsed, ...
sheet.Range("A1:A5").Cells(cell => cell.HasComment);
var usedBold = sheet.CellsUsed(x => x.Style.Font.Bold);
// Dimensions used
Assert.That(sheet.LastRowUsed(), Is.Null);
Assert.That(sheet.LastColumnUsed(), Is.Null);
ranger.Value = "pushing";
var usedRange = sheet.RangeUsed();
Assert.That(usedRange!.RangeAddress, Is.EqualTo(ranger.RangeAddress.ToString()));
// Offset: down 5 rows, right 10 columns
var movedRanger = sheet.Range(
ranger.FirstCell().CellBelow(5).CellRight(10),
ranger.LastCell().CellBelow(5).CellRight(10)
);
Assert.That(movedRanger.RangeAddress.ToString(), Is.EqualTo("K7:M10"));
movedRanger.Value = "Moved";
// Range has many functions:
// Union, Intersection, Intersects, Difference
using var workbook = new XLWorkbook();
var sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("MySheet");
// Format as text
sheet.Cell("A1").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "@";
// Numbers
sheet.Cell("B1").Value = 15.321;
sheet.Cell("B1").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "#,##0.00";
Assert.That(sheet.Cell("B1").GetFormattedString(), Is.EqualTo("15.32"));
Assert.That(sheet.Cell("B1").GetString(), Is.EqualTo("15.321"));
// Percentage
sheet.Cell("C1").Value = 0.5;
sheet.Cell("C1").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "0%";
Assert.That(sheet.Cell("C1").GetString(), Is.EqualTo("0.5"));
Assert.That(sheet.Cell("C1").GetFormattedString(), Is.EqualTo("50%"));
Assert.That(sheet.Cell("C1").Value, Is.EqualTo(0.5));
// Money
sheet.Cells("B2,D2").Value = 15000.23D;
sheet.Cells("C2,E2").Value = -2000.50D;
sheet.Range("B2:C2").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "#,##0.00 [$€-813];[Red]-#,##0.00 [$€-813]";
sheet.Range("D2:E2").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "[$$-409]#,##0";
// DateTime
sheet.Cell("B3").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "yyyy-mm-dd";
sheet.Cell("B3").FormulaA1 = $"=DATE({DateTime.Now:yyyy,MM,dd})";
sheet.Cells("C3,D3").Value = DateTime.Now;
sheet.Cell("C3").Style.NumberFormat.Format = DateTimeFormatInfo.CurrentInfo.FullDateTimePattern;
sheet.Cell("D3").Style.NumberFormat.Format = "dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm";
// Hyperlink
sheet.Cell("C24").SetHyperlink(new XLHyperlink("https://itenium.be"));
sheet.Cell("C24").Value = "Visit us";
// Internal hyperlink
workbook.Worksheets.Add("Data");
sheet.Cell("C26").SetHyperlink(new XLHyperlink("'Data'!A1", "(tooltip)"));
sheet.Cell("C26").Value = "Link to data sheet";
sheet.Cell("Z1").Clear();
using var workbook = new XLWorkbook();
var sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Styling");
// Cells with style
sheet.Cell("A1").Value = "Bold and proud";
sheet.Cell("A1").Style.Font.FontName = "Stencil";
sheet.Cell("A1").Style.Font.Bold = true;
sheet.Cell("A1").Style.Font.FontColor = XLColor.Green;
// Borders need to be made
sheet.Range("A1:A2").Style.Border.OutsideBorder = XLBorderStyleValues.Dotted;es.Dotted;
// Merge cells
sheet.Range(5, 5, 9, 8).Merge();
// More style
sheet.Cell("D14").Style.Alignment.ShrinkToFit = true;
sheet.Cell("D14").Style.Font.FontSize = 24;
sheet.Cell("D14").Value = "Shrinking for fit";
sheet.Cell("D15").Style.Alignment.WrapText = true;
sheet.Cell("D15").Value = "A wrap, yummy!";
sheet.Cell("D16").Value = "No wrap, ouch!";
// Background color
sheet.Cell("B5").Style.Fill.BackgroundColor = XLColor.Red;
// Horizontal Alignment
sheet.Cell("B5").Style.Alignment.Horizontal = XLAlignmentHorizontalValues.Center;
sheet.Cell("B5").Value = "I'm centered";
Because a picture is worth a 1000 words:
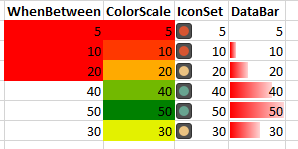
sheet.Cell("B3").Value = "WhenBetween";
sheet
.Range("B4:B9")
.AddConditionalFormat()
.WhenBetween(0, 20)
.Fill.SetBackgroundColor(XLColor.Red);
sheet.Cell("C3").Value = "ColorScale";
sheet
.Range("C4:C9")
.AddConditionalFormat()
.ColorScale()
.LowestValue(XLColor.Red)
.Midpoint(XLCFContentType.Percent, 50, XLColor.Yellow)
.HighestValue(XLColor.Green);
sheet.Cell("D3").Value = "IconSet";
sheet
.Range("D4:D9")
.AddConditionalFormat()
.IconSet(XLIconSetStyle.ThreeTrafficLights2)
.AddValue(XLCFIconSetOperator.EqualOrGreaterThan, 0, XLCFContentType.Number)
.AddValue(XLCFIconSetOperator.EqualOrGreaterThan, 20, XLCFContentType.Number)
.AddValue(XLCFIconSetOperator.EqualOrGreaterThan, 40, XLCFContentType.Number);
sheet.Cell("E3").Value = "DataBar";
sheet
.Range("E4:E9")
.AddConditionalFormat()
.DataBar(XLColor.Red)
.LowestValue()
.HighestValue();
using var workbook = new XLWorkbook("crash-if-not-exists.xlsx");
// Has overload to add a worksheet from another workbook
var sheet1 = workbook.AddWorksheet("Sheet1");
sheet1.ShowGridLines = false;
sheet1.ShowRowColHeaders = false;
// While possible to password protect a sheet, it's not possible
// to password protect an entire workbook.
sheet1.Protect("password");
// Position a new worksheet
var sheet0 = workbook.AddWorksheet("Sheet0", 0);
sheet0.TabColor = XLColor.Redwood;
sheet0.TabSelected = true;
sheet0.Visibility = XLWorksheetVisibility.Hidden;
sheet0.ActiveCell = sheet0.Cell("A5"); // or:
sheet0.Cell("A5").SetActive();
// Can only have one active cell but multiple can be selected
// sheet0.Cell("A5").Select();
// Freezing
sheet0.SheetView.FreezeRows(1);
sheet0.SheetView.FreezeColumns(4);
sheet0.Column(1).Hide();
// Copy to same/other workbook:
sheet1.CopyTo(workbook, "Copy");
// workbook.SaveAs(Stream / string);
// Overload to validate & evaluate formulas
There are small nugets available for delivering the Excel in ASP.NET, MVC and WebApi environments.
Find the implementation for WebApi here.
public static class Extensions
{
private const string ContentType = "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet";
public static FileStreamResult Deliver(this IXLWorkbook workbook, string fileName)
{
var memoryStream = new MemoryStream();
workbook.SaveAs(memoryStream);
memoryStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
return new FileStreamResult(memoryStream, ContentType) { FileDownloadName = fileName };
}
}
Just some handy tidbits.
public static class ExcelExtensions
{
public static IXLDataValidation SetDropdownList(this IXLCell cell, IEnumerable<string> options)
{
var validation = cell.CreateDataValidation();
validation.AllowedValues = XLAllowedValues.List;
validation.InCellDropdown = true;
validation.IgnoreBlanks = true;
// ATTN: must start/end with a double quote (")
validation.List($""{string.Join(",", options)}"");
return validation;
}
public static IXLCell SetHyperlink(this IXLCell cell, string url, string text, string? tooltip = null)
{
cell.SetValue(text).SetHyperlink(new XLHyperlink(url, tooltip));
return cell;
}
public static IXLStyle SetNumberFormatId(this IXLNumberFormat nf, XLPredefinedFormat.Number format)
{
return nf.SetNumberFormatId((int)format);
}
public static IXLStyle SetNumberFormatId(this IXLNumberFormat nf, XLPredefinedFormat.DateTime format)
{
return nf.SetNumberFormatId((int)format);
}
}
Stuff that came into being during the making of this post
Other interesting reads
